How to Order ? Simple.
-

1.
Select Treatment
Choose from our treatment options or speak to the in-store pharmacist for advice
-

2.
Complete Medical Questionnaire
Complete our free online medical consultation to be reviewed by our Clinical Team
-

3.
Collect Medication from Local Pharmacy
We will notify you when your medication is ready for collection
Advice for Fungal Skin Infection
Many different fungi and yeasts can cause infections of your skin, hair, and nails. Many fungal infections are contagious (can be spread from person to person). You can get a fungal infection in the following ways:
- Through direct contact with an infected person or animal, including pets like dogs and cats.
- Sharing items such as clothes, towels, hairbrushes or bedding with an infected person.
- More rarely, from contact with soil.
- If fungi that normally live harmlessly in or on your body grow out of control.
Fungal infections are more likely in areas of your body that are warm or moist. This means you’re more likely to get an infection if you:
- Live or work in a hot or humid environment
- Wear tight-fitting clothing or shoes that don’t let your feet ‘breathe’
- Tend to sweat lots
- Are obese with skin folds that rub against each other
You’re also more likely to develop a fungal skin infection if you:
- Have a weakened immune system due to illness like HIV, or to taking medicines like corticosteroids
- Have diabetes
- Have other conditions affecting your skin – for example, psoriasis or eczema
Having a weakened immune system may also mean the infection is more severe and harder to treat.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is usually based on the appearance of the skin and medical history. In some cases, skin scrapings, nail clippings, or hair samples may be examined under a microscope or cultured in a lab to identify the specific fungus.
Types of fungal skin infections
Here we describe some of the main types of fungal infection that can affect your skin and nails.
Athlete’s foot
This is the most common type of fungal infection. It affects around 7 in 10 people at some point in their lives. It’s caused by a fungus that grows in the skin between your toes and on the soles of your feet. It grows easily here because the area gets moist when your feet sweat.
Athlete’s foot can cause itchy, white, flaky patches on the skin between your toes. It may sometimes look red on white skin and cause darker patches on black or brown skin. It can cause painful cracks or fissures between your toes too. The sole of your foot can also become itchy, thickened, and scaly. You might also get blisters.
Athlete’s foot is more likely if you wear shoes that make your feet sweaty and you’re in a warm, humid environment. You can catch it by walking barefoot in shared shower or swimming areas. If you scratch the affected area, it can spread the infection to other parts of your body.
Ringworm
Despite its name, ringworm is an infection with a fungus not a worm. It gets its name because it often causes a ring-shaped rash. Ringworm infections are common, especially in children and young adults. They can affect different parts of your body.
Ringworm on your body
This causes scaly, ring-shaped patches of skin on areas of your body including your arms, legs and trunk. These may get bigger, and you may have several overlapping patches. The affected areas may look red on white skin and appear as darker patches on black or brown skin. You can catch ringworm by touching somebody who already has it or from contact with contaminated items such as clothing or bedding. You can also catch the infection from infected animals, including cats and dogs.
Ringworm in your groin
Ringworm in your groin causes an itchy rash in your groin and around the top of your legs. This may appear red on white skin or as darker areas on black or brown skin. Also called ‘jock itch’, it’s more common in men than women. You usually get ringworm in your groin if you have fungal infections affecting other parts of your body – for example, your feet or nails. This then spreads to your groin.
Ringworm on your scalp
You can get this at any age, but it mostly affects children. It causes scaly, itchy patches on your scalp and circular patches of hair loss. You may also notice black dots on your scalp. These are broken hair stubs. In some people, the patches become inflamed, with pus-filled spots. You may develop a crusty, pus-filled area on your scalp called a ‘kerion’. You can get ringworm on your scalp by direct contact with someone who has the infection. You can also get it by sharing contaminated items such as hairbrushes or clothing.
Candida (yeast) Skin Infection
Candida is a yeast, which is a kind of fungus. It usually lives harmlessly inside your digestive system or vagina. But if conditions are right, Candida can multiply and start to cause symptoms. These yeast infections most often appear around your genitals (vagina or penis), in your mouth, or where you have folds of skin. A common name for Candida infections is ‘thrush’. In the vagina, it’s called vaginal thrush. Candida skin infections most often affects the areas around your groin, underneath your breasts, and in your armpits. It makes the affected area sore and itchy. Your skin may become scaly and covered with a white–yellow substance. In skin folds, the skin is usually red and moist, and small pus-filled spots may appear.
Pityriasis Versicolor
This is caused by a type of yeast called Malassezia, which usually lives harmlessly on your skin. It typically affects teenagers and young adults. Pityriasis versicolor causes patches of discoloured skin with a fine scale, that are sometimes itchy. It most commonly appears on your back, chest, or upper arms but it can affect other areas. Patches can be pink, brown, red, or almost white. If you have a light skin tone, you may notice the affected area doesn’t tan as much as the rest of your skin in summer. If you have darker skin, the affected area may look paler.
The symptoms of a fungal skin infection depend on the type of fungus that’s caused it, and where it is. You may notice changes in your skin, hair, or nails. The fungus can affect just one area or several areas of your body. Fungal infections can also spread from one area of your body to another.
Fungal infections of your skin can change how it looks. You may get patches of skin that are:
- Red, scaly, or itchy patches on the skin
- Blisters or pustules
- Cracking or peeling skin
- Discolored, thickened, or brittle nails
- Hair loss in affected areas
Fungal skin infections occur when fungi invade and multiply on the skin, hair, or nails. The primary causes can be categorized based on the type of fungi and the conditions that promote their growth.
Types of Fungi
Dermatophytes:
- Common Species: Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton.
- Infections: Athlete's foot, jock itch, ringworm, scalp ringworm, and nail fungus.
- Mode of Infection: Dermatophytes feed on keratin, a protein found in the skin, hair, and nails. They thrive in warm, moist environments.
Candida:
- Common Species: Candida albicans.
- Infections: Oral thrush, vaginal yeast infection, intertrigo.
- Mode of Infection: Candida is a yeast that naturally resides in the human body. Overgrowth can occur when the natural balance of microorganisms is disrupted.
Malassezia:
- Common Species: Malassezia furfur.
- Infections: Pityriasis versicolor.
- Mode of Infection: Malassezia is a yeast that is part of the normal skin flora but can overgrow in certain conditions.
Contributing Factors
Environmental Factors:
- Warm and Humid Conditions: Fungi thrive in environments that are warm and moist, making infections more common in hot and humid climates.
- Poor Ventilation: Wearing tight or non-breathable clothing can create a warm, moist environment conducive to fungal growth.
Personal Hygiene:
- Excessive Sweating: Sweating creates a moist environment that can promote fungal growth.
- Poor Hygiene Practices: Infrequent bathing or not drying off completely can leave the skin moist, fostering fungal growth.
- Sharing Personal Items: Sharing towels, clothes, or shoes can transmit fungal spores from one person to another.
Medical Conditions:
- Immunocompromised Individuals: Conditions like HIV/AIDS, diabetes, or the use of immunosuppressive drugs can weaken the immune system, making it easier for fungi to cause infections.
- Hormonal Changes: Changes in hormone levels, such as during pregnancy or with the use of oral contraceptives, can disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms, leading to fungal overgrowth.
Lifestyle Factors:
- Occupation and Hobbies: Activities that involve prolonged exposure to moist environments (e.g., swimming, gardening) can increase the risk of fungal infections.
- Tight Clothing and Footwear: Wearing tight shoes or clothes can trap moisture and create a breeding ground for fungi.
Skin Integrity:
- Minor Skin Injuries: Cuts, scrapes, or other minor injuries can provide an entry point for fungi.
- Skin Conditions: Pre-existing skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis can compromise the skin barrier, making it easier for fungi to invade.
Topical antifungals for fungal skin infections come in various forms. These include creams, lotions, and shampoos. Most fungal skin infections can be treated with topical antifungals cream. Many of the treatments are available over the counter from a pharmacist, so you don’t need a prescription from your doctor.
You’ll usually need to continue treatment for one to two weeks after your symptoms have gone, to make sure the infection doesn’t come back. You may need to continue topical treatment for fungal nail infection for up to a year.
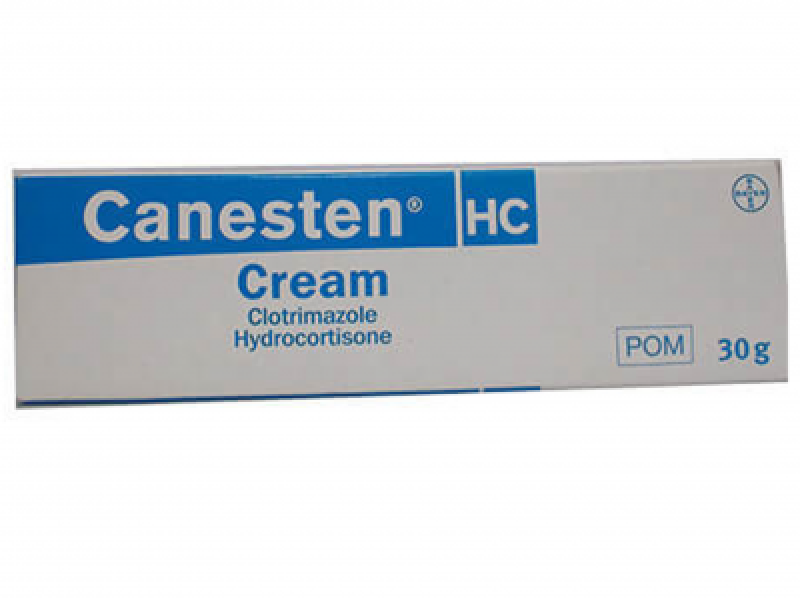
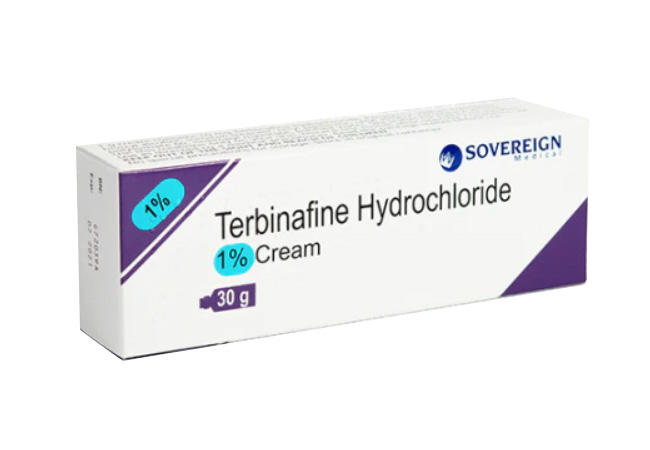
Depending on the severity and duration, you may need prescription topical antifungal cream. At Pharmacinta, we provide Canestan HC Cream and Terbinafine 1% Cream.
While antifungal medications (both topical and oral) are the primary treatment for fungal skin infections, there are several other approaches and adjunctive treatments that can be effective. These include home remedies, lifestyle modifications, and preventive measures to support healing and prevent recurrence.
Many different fungi and yeasts can cause infections of your skin, hair, and nails. Many fungal infections are contagious (can be spread from person to person). You can get a fungal infection in the following ways:
- Through direct contact with an infected person or animal, including pets like dogs and cats.
- Sharing items such as clothes, towels, hairbrushes or bedding with an infected person.
- More rarely, from contact with soil.
- If fungi that normally live harmlessly in or on your body grow out of control.
Fungal infections are more likely in areas of your body that are warm or moist. This means you’re more likely to get an infection if you:
- Live or work in a hot or humid environment
- Wear tight-fitting clothing or shoes that don’t let your feet ‘breathe’
- Tend to sweat lots
- Are obese with skin folds that rub against each other
You’re also more likely to develop a fungal skin infection if you:
- Have a weakened immune system due to illness like HIV, or to taking medicines like corticosteroids
- Have diabetes
- Have other conditions affecting your skin – for example, psoriasis or eczema
Having a weakened immune system may also mean the infection is more severe and harder to treat.
Home Remedies
- Tea Tree Oil: Has natural antifungal properties. Apply diluted tea tree oil to the affected area a few times daily.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Known for its antifungal and antibacterial properties. Dilute with water and apply to the infected area.
- Coconut Oil: Contains caprylic acid and lauric acid, which have antifungal properties. Apply directly to the skin.
- Aloe Vera: Known for its soothing and healing properties. Apply aloe vera gel to reduce itching and inflammation.
- Garlic: Contains allicin, an antifungal compound. Apply crushed garlic mixed with coconut oil to the affected area.
- Epsom Salt Soak: Helps to relieve itching and dry out the infection. Soak the affected area in an Epsom salt solution.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Good Hygiene Practices: Regularly wash and thoroughly dry the affected areas. Change clothes, socks, and underwear daily.
- Keep Skin Dry: Moisture promotes fungal growth. Use talcum powder or antifungal powder to keep areas dry, especially in skin folds.
- Wear Loose-Fitting Clothes: Opt for breathable fabrics like cotton to reduce sweating and moisture buildup.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share towels, clothing, or footwear to prevent spreading the infection.
- Proper Footwear: Wear sandals or flip-flops in communal areas like locker rooms and showers to avoid contact with fungi.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Treatments
- Antifungal Creams and Ointments: OTC options like clotrimazole, miconazole, and terbinafine are effective for treating mild infections.
- Antifungal Powders and Sprays: Useful for keeping areas dry and preventing recurrence, especially for athlete’s foot.
Prescription Treatments
- Topical Steroids: Used in combination with antifungal medications to reduce severe inflammation and itching.
- Oral Antifungals: For more severe or widespread infections, prescription oral antifungals like itraconazole or griseofulvin may be necessary.
- Medicated Shampoos: For scalp infections, medicated shampoos containing ketoconazole or selenium sulfide can be effective.
Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Probiotics: Taking probiotic supplements or eating probiotic-rich foods like yogurt may help maintain a healthy balance of microorganisms and prevent fungal overgrowth.
- Herbal Remedies: Herbs like neem, oregano oil, and calendula have antifungal properties and can be used as natural treatments.
Preventive Measures
- Maintain Healthy Skin: Regular moisturizing to avoid cracks and fissures that can serve as entry points for fungi.
- Balanced Diet: Eating a balanced diet to support immune function and overall skin health.
- Regular Monitoring: Keep an eye on any recurring symptoms and consult a healthcare provider promptly if an infection is suspected.
Frequently Asked Questions
Fungal skin infections are caused by fungi that infect the skin, hair, or nails. Common infections include athlete's foot, ringworm, jock itch, and candidiasis.
They are caused by fungi such as dermatophytes, Candida, and Malassezia, which thrive in warm, moist environments. Poor hygiene, tight clothing, and sharing personal items can increase the risk.
Maintain good hygiene, keep your skin dry, wear breathable clothing, avoid walking barefoot in communal areas, and don't share personal items like towels and shoes.
Symptoms include red, scaly, or itchy patches; blisters; cracked skin; discolored nails; and hair loss in affected areas.
Diagnosis is typically based on the appearance of the skin and medical history. Skin scrapings, nail clippings, or hair samples may be examined under a microscope or cultured in a lab.
Treatments include topical antifungal creams, oral antifungal medications, good hygiene practices, and home remedies like tea tree oil and apple cider vinegar.
Yes, home remedies include applying diluted tea tree oil, apple cider vinegar, coconut oil, aloe vera gel, and crushed garlic mixed with coconut oil to the affected area.
See a doctor if the infection is severe, widespread, or doesn't improve with over-the-counter treatments, or if you have a weakened immune system.
Yes, fungal infections can spread if not treated properly. Avoid scratching the infected area and practice good hygiene to prevent spreading.
Yes, over-the-counter antifungal creams, powders, and sprays can be effective for mild infections. However, severe or persistent infections may require prescription medications.
Yes, fungal skin infections can recur, especially if preventive measures are not followed. Maintaining good hygiene and keeping the skin dry are crucial in preventing recurrences.
Yes, they can be contagious. They can spread through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person or animal, or by sharing contaminated items like towels, clothing, or shoes.
The healing time varies depending on the type of infection and its severity. Mild infections may clear up in a few weeks with treatment, while more severe cases can take several months.
You can exercise, but it's important to keep the affected area clean and dry. Wear loose, breathable clothing and shower immediately after exercising to prevent worsening the infection.
Yes, they are more common in warm, humid climates where fungi thrive. People living in such climates should take extra precautions to keep their skin dry and clean.
A balanced diet can support your immune system, which helps in fighting infections. Some believe that reducing sugar intake may help, as fungi feed on sugar, but this is not universally proven.
Many topical antifungal treatments are considered safe during pregnancy, but you should always consult your healthcare provider before using any medication.
If left untreated, fungal infections can lead to secondary bacterial infections and other complications, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems.
Signs of improvement include reduced redness, scaling, and itching, and the healing of blisters or cracks. If symptoms persist or worsen, consult your healthcare provider.
Topical antifungal treatments may cause mild side effects like skin irritation or redness. Oral antifungal medications can have more significant side effects, such as liver toxicity or gastrointestinal issues. Always follow your doctor's instructions and report any unusual symptoms.
Yes, pets can also get fungal infections like ringworm, which can be transmitted to humans. If your pet shows signs of a skin infection, take them to a veterinarian.
Regularly clean and disinfect surfaces, wash bedding and clothing in hot water, and avoid sharing personal items. Use antifungal sprays or solutions to clean areas that may harbor fungi.
Stress can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections, including fungal skin infections. Managing stress through relaxation techniques and a healthy lifestyle can help.
Yes, fungal infections can sometimes be mistaken for other skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis. A proper diagnosis by a healthcare professional is essential for effective treatment.
Yes, children are susceptible to fungal infections, especially ringworm and scalp infections. Good hygiene practices and avoiding sharing personal items can help prevent infections in children.
Canesten HC Cream is a combination antifungal and anti-inflammatory cream that contains clotrimazole and hydrocortisone. It is used to treat fungal skin infections accompanied by inflammation and itching.
Clotrimazole is an antifungal agent that inhibits the growth of fungi, while hydrocortisone is a mild corticosteroid that reduces inflammation, redness, and itching.
It is used to treat fungal infections like athlete's foot, jock itch, and ringworm, particularly when these conditions are accompanied by inflammation and itching.
Consult a healthcare provider before using Canesten HC Cream on children, as it contains hydrocortisone, which should be used with caution in pediatric patients.
Consult your healthcare provider before using Canesten HC Cream if you are pregnant or breastfeeding to ensure it is safe for you.
Use the cream for the full course of treatment as prescribed by your healthcare provider, typically not exceeding 7 days unless directed otherwise.
Avoid contact with eyes, mouth, and mucous membranes. Do not use on broken skin or large areas of the body without medical advice.
Terbinafine Cream is an antifungal medication used to treat various fungal skin infections such as athlete's foot, jock itch, and ringworm.
Terbinafine inhibits the growth of fungi by interfering with their cell membrane formation, effectively killing the fungal cells.
It is used to treat fungal infections like athlete's foot, jock itch, ringworm, and fungal nail infections.
Consult a healthcare provider before using Terbinafine Cream on children, as the safety and effectiveness may vary.
Consult your healthcare provider before using Terbinafine Cream if you are pregnant or breastfeeding to ensure it is safe for you.
Use the cream for the full course of treatment as prescribed by your healthcare provider, typically 1 to 2 weeks for most infections, but the duration may vary.
Avoid contact with eyes, mouth, and mucous membranes. Do not use on broken skin or large areas of the body without medical advice.