How to Order ? Simple.
-

1.
Select Treatment
Choose from our treatment options or speak to the in-store pharmacist for advice
-

2.
Complete Medical Questionnaire
Complete our free online medical consultation to be reviewed by our Clinical Team
-

3.
Collect Medication from Local Pharmacy
We will notify you when your medication is ready for collection
Advice for Allergies
Allergies affect around 1 in 4 people in the UK and many people (both young and old) suffer from this condition. It's possible to develop allergies at any point in your life, and symptoms can vary in severity for a number of reasons. Causes can vary, but many allergies are manageable, and should not affect your daily life if the proper precautions are taken. While avoiding the allergens that trigger your reaction is the best way to stay healthy, you can manage your symptoms effectively with treatment.
An allergic reaction happens because of the immune system. In people with allergies, the immune system reacts to certain substances like pollen and dust as though they’re harmful, and releases chemicals like histamine to protect the body. Whenever the body is exposed to that same allergen, the immune response leads to allergic symptoms like runny or blocked nose, asthma or coughing fits, inflammation or irritation of the eyes, skin irritation, and swelling of the skin, lips or tongue.
Common substances that can produce an allergic reaction include foods like shellfish, nuts, milk, and eggs, as well as pollen, mould, dust, and animal dander.
In extreme situations, allergic reactions can cause anaphylactic shock. This is when your body reacts very badly and very quickly to a particular allergen (e.g. nuts, dairy products, fish etc.). Symptoms include swelling of the hands, eyes and feet, itchy skin, stomach pains, and tightening of the airways.
Anaphylaxis can cause swelling of the lips and tongue, breathing problems, collapse, and loss of consciousness. In some cases, anaphylaxis causes death, meaning it must always be treated as a medical emergency.
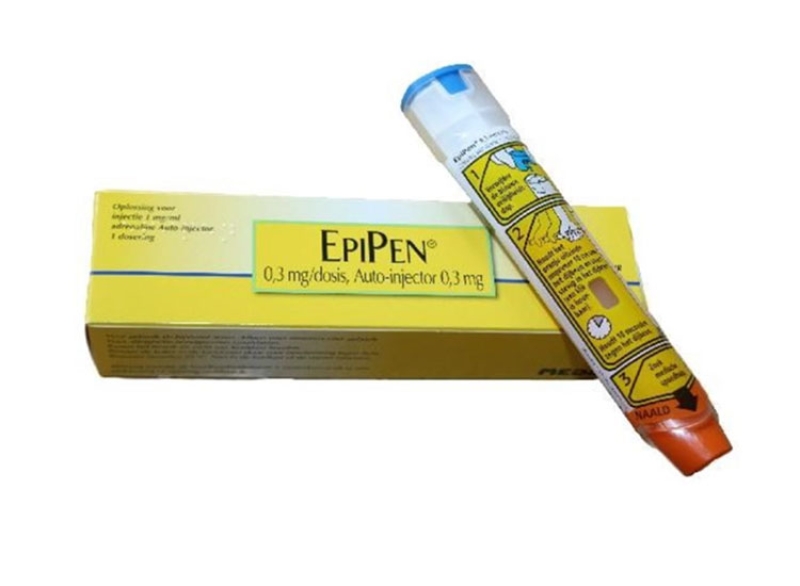
At Pharmacinta, we can prescribe the prescription antihistamine medication for seasonal allergic rhinitis, which many people experience as hay fever symptoms. For severe allergies, if you've already been prescribed an EpiPen by your doctor, we can prescribe 1 or 2 pens.
Common symptoms of an allergic reaction include:
- sneezing
- coughing
- sinus pain
- swelling
- itchy mouth, throat, eyes and ears
- shortness of breath
- nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea
Some allergic reactions may simply be inconvenient, such as hay fever, but others, such as peanut allergy, can be fatal if not treated medically.
Symptoms of anaphylaxis include:
- Airway: swelling in the throat, tongue or upper airways (tightening of the throat, hoarse voice, difficulty swallowing)
- Breathing: sudden onset wheezing, breathing difficulty, noisy breathing
- Circulation: dizziness, feeling faint, sudden sleepiness, tiredness, confusion, pale clammy skin, loss of consciousness
Any one of these means you should use your adrenaline auto-injector and call 999.
You might have milder allergy symptoms alongside too, like an itchy throat or swelling of your lips. Even if you’ve had these before, take notice of the severe anaphylaxis symptoms above. Still use your auto-injector.
Research has shown that there are a number of risk factors which increase a person’s chances of having an allergy:
Genetics - Normally, a child has a one in five chance of developing an allergy. However, the risk is doubled in children who have one parent with allergies. If both parents have allergies, there is a 60-80% chance that the child will develop them too.
Asthma and other allergies - Having asthma increases your chance of developing an allergy. Furthermore, having one type of allergy increases the chances of becoming allergic to something else.
Hay fever (allergy to tree, flower and grass pollen) tends to be seasonal, affecting people more in spring and summer. Understanding what causes your allergies is important so that you can avoid them and be prepared with appropriate treatment.
If you develop an allergy, you can try to identify what has caused it by thinking about what has changed in your lifestyle. Are you using a new medicine or cosmetic product? Have you been in contact with animals or eaten new food? Try avoiding the suspected trigger for a week and see if your symptoms improve.
If you're unable to identify what's causing a reaction, speak to your GP about allergy testing. In a safe environment, you will be tested for a skin reaction to a range of allergens. Once identified, you can know to avoid these triggers.
Anaphylaxis is caused by the body’s immune system overreacting to an allergic trigger.Some common triggers include:
- Foods – particularly nuts, milk, eggs, shellfish and some fruits
- Medicines – such as some antibiotics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin
- Insect stings – particularly bee or wasp stings
- Latex – found in gloves and condoms
There are various possible triggers of anaphylaxis such as food, medicines, and venom from insect stings. Although in some cases of anaphylaxis, the cause is hard to identify.
The most commonly implicated medicines in anaphylaxis in the UK are anaesthetics, antibiotics (like penicillin), aspirin, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).Commonly implicated food triggers include:Nuts,Peanuts, Sesameseeds, Mustard, Milk, Fish, Eggs.
There are many different ways to treat allergies. It is important to try and establish what the cause of your allergic reactions are, as this will help identify the most suitable treatment and also help with managing triggers.
It is worth noting that it is often impossible to avoid allergens altogether and there are a number of medicines and allergy treatments that can relieve symptoms when they occur.
Antihistamines are probably the best known type of allergy medicine, and most are available from a pharmacy without a prescription. These medicines work by blocking the action of histamine, which is the chemical that causes symptoms during an allergic reaction. For many, the over the counter antihistamine is not as effective, and therefore a prescription antihistamine is available in the form of Fexofenadine 180mg, which is usually more effective.
Adrenaline (EpiPen) is used to treat severe allergic reactions such as those to peanuts and wasp stings. In these cases, the sufferer can go into anaphylactic shock when the sudden high levels of histamine can cause difficulty breathing, and even loss of consciousness. Adrenaline is administered via an injection (such as EpiPen), which should be carried at all times by people who have severe allergies.
Adrenaline injection can help stop an anaphylactic reaction from progressing and becoming life-threatening. An adrenaline auto-injector should be used as soon as you suspect a serious reaction. You should always call 999 if you think you, or someone else, has symptoms of anaphylaxis. You should carry 2 injectors at all times. The reason for this is you may have to inject a second dose of adrenaline 5-15 minutes after the first dose if symptoms don’t improve.
Lifestyle Changes
Being prepared is the most important thing. Whether you have hay fever, asthma, or another allergy, having the necessary measures to prevent and minimise the likelihood of an allergic reaction will allow you to live life as normally as possible.
Usually, simply avoiding certain foods, environments or animals will be enough to avoid an allergic reaction. Taking medicines is another preventative measure which can be done either before symptoms start, or as they are just beginning.
If you know what the cause of your allergic rhinitis is, trying to limit your exposure to this allergen should help reduce your symptoms. Regular cleaning of the nasal passages with a salt water solution should also help keep your nose free of irritants.
Some people use steroid nasal sprays to help manage their allergic rhinitis symptoms. You could also combine Fexofenadine with a steroid nasal spray or decongestant.
Frequently Asked Questions
In medicine, the label "intolerance" refers to a sensitivity to a substance you've consumed. An allergy, meanwhile, can be brought on by any kind of exposure. You might have an allergic reaction after eating, breathing in, or touching the substance you're allergic to. Another important difference between the two is that allergies can lead to anaphylaxis and be life-threatening. Intolerances are not life-threatening, although they can cause unpleasant symptoms.
There are a few different types of allergy test, but the basic idea is to work out what's causing your allergy and how severe it is. The tests will be designed to look for different types of allergy which affect the body in different ways, according to the symptoms you've been having. Skin prick tests are where a drop of liquid containing an allergen is placed on the skin. The same area of skin is then gently pricked with a needle. If you have an allergy to that particular substance, an itchy red bump will appear where your skin was pricked within about 15 minutes. Blood tests can be used to check whether your body has created antibodies in response to specific allergens. Elimination diets are used to find food allergies. Certain foods are removed from your diet one by one, then gradually reintroduced. Challenge testing is also used to find food allergies. This is a supervised test where you eat increasing amounts of the suspected allergen.
Yes, but a food intolerance is not the same as an allergy, so the tests are completely different. In people with food intolerances, the body simply has trouble digesting a specific substance. A test for lactose intolerance may not be needed, your GP may simply advise that you cut dairy from your diet for a couple of weeks to see if your symptoms improve.
There is currently no diagnostic test for wheat intolerance, so the best way to find out if you have an intolerance is to try cutting out wheat products from your diet.
You might need allergy tests if your symptoms are very severe and/or it's not clear what you're allergic to.
If your GP provides a referral, you can get tested at a specialist NHS allergy clinic. You can also get tested at a private clinic, and pay for your own allergy tests.
A food allergy is when the body's immune system reacts unusually to specific foods. Although allergic reactions are often mild, they can be very serious. In the most serious cases, a person has a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis), which can be life threatening.
There are 3 key things to be on top of when it comes to managing a food allergy: Identify and avoid the cause (if possible) Recognise the symptoms of an allergic reaction by keeping a food diary Know what to do if it happens again Treatment for a food allergy
The most common allergens include dust mites, mold/mold spores, pollen, animal dander, cockroaches, peanuts, milk, eggs, latex, and penicillin. The dust mite is the most common cause of allergies, but food allergies have risen in recent years.
An allergist or immunologist can diagnose your allergies using allergy skin tests, which show if your immune system reacts to specific allergens. Blood tests can also show the presence of antibodies, which indicate a sensitivity. Testing alone though is NOT a proper diagnosis of an allergy. Beyond tests, your personal medical history and family medical history are also factored in with your conditions in your environment to get a more complete view of the situation and make a proper diagnosis.
The most common allergic diseases are allergic rhinitis (hay fever), asthma, allergic dermatitis (eczema), contact dermatitis, food allergy, and urticaria (hives). Allergic disease can be classified by the type of allergen (i.e., food allergy) or by the part of the body that is affected. For example, if allergic symptoms appear in your nose, you are said to have allergic rhinitis. If allergic symptoms appear in your lungs, then you have asthma.
There is a genetic factor in the development of allergic disease. If one parent has allergic disease, the estimated risk of a child to develop allergies is 48%; the child's estimated risk grows to 70% if both parents have a history of allergies.
The genetic factor does not explain why the incidence of allergy and asthma is rapidly increasing in the modern world. There are a few theories about why allergic disease is growing. One theory blames our increasing immune system sensitivity on the abundance of synthetic chemicals in our modern world. Another theory, known as the hygiene hypothesis, posits that the human immune system is becoming more reactive to allergens because of modern hygiene and healthcare.
People with seasonal allergic rhinitis (hay fever) only experience symptoms during the time of year when certain allergens are in the air outdoors. When most people talk about allergy season, they're referring to springtime, when plants bloom and pollen counts soar. Perennial allergies, or year-round allergies, are typically caused by indoor allergies to dust mites, mold, cockroaches, and pet dander.
People often grow into allergies, particularly environmental allergies. Some children outgrow food allergies after long periods of avoiding the allergen, and up to half of young children outgrow their asthma, but many find that the symptoms return later in life.
Allergic reactions can develop at any age, no matter how old you are. If someone's total allergen load reaches its maximum point, then s/he will most likely develop allergies.
Anaphylaxis is the most severe and potentially fatal end of the allergic reaction spectrum. Fatal anaphylaxis normally occurs because of extreme allergic reactions to foods such as shellfish, cod, or peanuts. Penicillin is the most common culprit in death from drug allergy.
The most common foods behind allergic reactions include nuts, peanuts, milk, egg, wheat, and soybean proteins.
Allergen avoidance is currently the best treatment for any allergic disease. Avoid the allergen, and you'll avoid the allergic reaction. Diagnosis and education are crucial steps in allergen avoidance. Educated allergy and asthma sufferers fare much better than those who do not understand their disease.
Telfast is the branded name for generic Fexofenadine. Telfast and Fexofenadine are medically equivalent: they both contain the same amount of the active ingredient fexofenadine hydrochloride. The main difference is that the generic Fexofenadine version is cheaper than the branded version, Telfast.
You can buy hay fever tablets in the UK online and over the counter. However, certain hay fever tablets like desloratadine and levocetirizine are only available on prescription.
Fexofenadine is an effective antihistamine and is considered to be a non-sedating antihistamine.
Medicines can work differently for everyone. Some people may find fexofenadine is better than cetirizine but other people will find the opposite.
One tablet will have a beneficial effect for around 24 hours. The antihistamine effect starts around 1 hour after taking a dose, peaks after around 6 hours and is effective for around 24 hours.
The recommended dose for hay fever is one tablet once a day. In some circumstances, your doctor may prescribe higher doses for you but this significantly increases the risk of side effects.
Fexofenadine hydrochloride in the UK is used to improve hay fever symptoms. It can also be prescribed to treat other medical conditions like hives, certain food allergies, and insect bites and stings.
All antihistamines have a chance of producing drowsiness, though this can vary from person to person. All of the once-daily antihistamines, frequently called non-sedative antihistamines, have a lot lower incidence of drowsiness compared to the older types of antihistamine (such as chlorphenamine).
Newer once-daily antihistamine tablets are not addictive and they are safe to use for long periods of time. Older antihistamines that are used for nausea and insomnia can produce some dependency when used for long periods.